Remember when GDPR first went into effect in 2018? Or when CCPA brought the data privacy conversation to the U.S. in 2020?
There was a lot of noise. But in the end, organizations didn’t do as much as they should have to prepare for this changing legislation because they assumed they would just cross the bridge when the time came.
The time has come.
Now that the legislation dust has settled, authorities are ramping up enforcement. Organizations can no longer sweep privacy compliance under the rug as more infractions make the news.
Some organizations have realized that the patchwork measures they tacked on a few years ago are falling apart. They must revisit their technology and workflows to mitigate risks by age of data privacy, ushering in the rise of consumer awareness and privacy needs. Today, business values (i.e. efficiency, innovation, customer loyalty) are closely associated with privacy maturity.
Privacy compliance should be a core requirement of mapping sensitive data and implementing processes to secure sensitive data. It comes down to how you:
- Architect the data infrastructure in your organization.
- Map and tag sensitive customer information.
- Ensure sensitive data has the right checks and balances with a data governance framework.
3 Key Areas To Cover in Privacy Compliance
Privacy compliance isn’t just about securing customer data by locking it in a vault. You must consider how you can generate insights from the information and process data subject requests (DSRs) promptly, efficiently, and at scale.
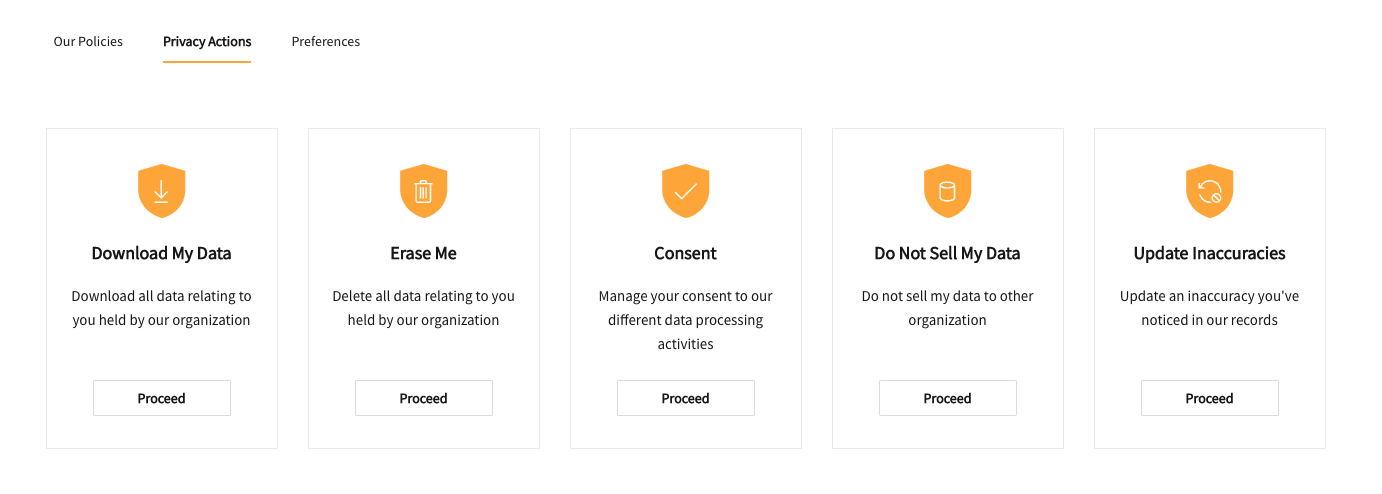
Types of DSRs include:
- Download My Data
- Erase Me
- Consent
- Do Not Sell My Data
- Update Inaccuracies
Here are three areas to cover when building privacy compliance into your data architecture and processes:
1. Automation
Most data privacy regulations require organizations to have the capability to delete a customer’s record upon request. While removing the data from your systems checks the compliance box, you lose all the data you could use for aggregated analytics to generate insights.
A key nuance is that you can keep the information for analytics if it’s anonymized—you don’t have to delete the data if it can’t be associated with an individual. But doing so manually isn’t realistic because the process is time-consuming and error-prone.
Using automation technology, you’re able to anonymize data throughout your databases and infrastructure at scale to ensure the process is done right every time. You can also handle DSRs efficiently, freeing employees to focus on delivering value instead of digging through records.
To set the stage for successful automation, you must take inventory of all your data sources and built pipelines that target the right sensitive data without creating issues for the source systems. Data mapping and ongoing governance should be an integral part of the process when setting up your data warehouse and infrastructure.
2. Workflows
Automation could amplify errors, issues, and inefficiencies if your workflows aren’t optimized.
For example, if your system incorrectly identifies a user and deletes or anonymizes someone else’s data—you’re in a pickle. You must implement processes that verify a user’s identity before doing anything with their record.
Additionally, your workflows must account for various DSRs. A consumer may ask you to:
- Confirm what data you have about them and in which systems.
- Update inaccurate or outdated information you have in their record.
- Review or change the consent on how you use their data.
- Allow them to access their information in a downloadable format.
- Not share or sell their data with other organizations.
- Delete or anonymize their data in your systems.
The good news is that you don’t need to reinvent the wheel and set up these workflows from scratch. The right tools and technologies can guide your team through the process, show you where each request is in the pipeline, and ensure you’re deleting or anonymizing the correct records for the right reasons.
3. Auditability
The final and arguably most critical component in privacy compliance is the ability to prove to consumers or authorities that you have taken action to fulfill a DSR. You must be able to show that a user’s data or consent is anonymized, deleted, or updated per their request.
Keeping an audit trail of all the steps you have taken to comply with DSRs should be an integral part of your privacy compliance workflows. These logs are essential if you run into legal issues and must prove that you have followed the proper procedures to adhere to regulations and protect consumer privacy.
Implementing Privacy Compliance in 2023
The three key factors of privacy compliance affect many aspects of your operations and must become an integral part of your data infrastructure and governance framework. But as organizations process and leverage more customer data, it’s increasingly challenging to stay compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and other upcoming legislations with ad hoc solutions.
Our Modern Data Stack Platform supports a privacy-first approach to data management and accessibility to ensure privacy compliance across business initiatives. You can centralize all your customer data and use our consent management capabilities to automate DSRs and ensure you connect with customers via their preferred methods with audibility built in.
Request a demo to see how we can help you ensure privacy compliance while delivering an outstanding customer experience.