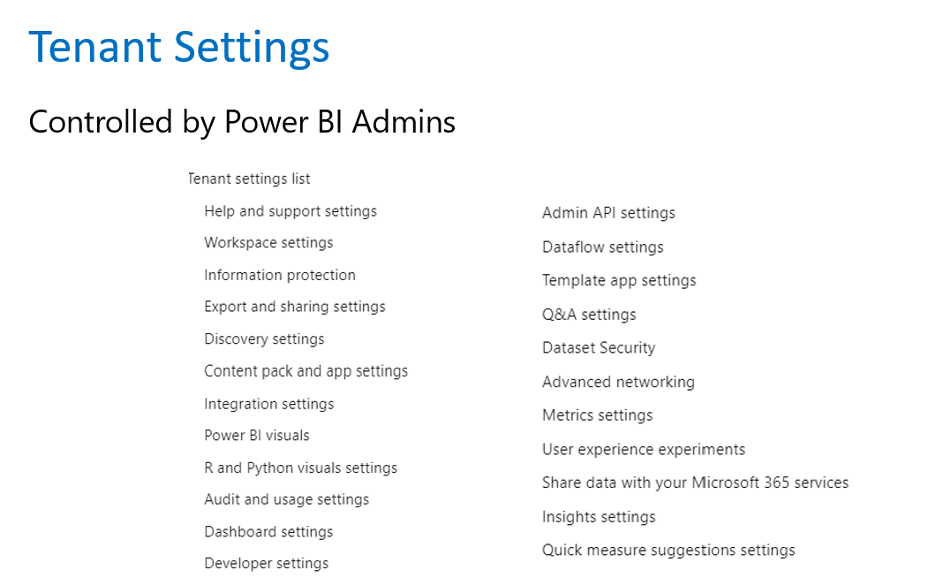
Security and governance are two of the most critical considerations in enabling a successful Power BI environment. But due to the complex nature of the platform, there are often several points of confusion that pop up for users.
While the Power BI platform itself has had minimal vulnerabilities in the past two years, breakdowns in user processes surrounding Power BI security can lead to headaches and potential risks for organizations.
An understanding of some of these advanced governance and security concerns can turn any Power BI user into a savvy data manager.
We’ve gathered some of the most common questions we hear from our clients to help you effectively secure your Power BI environments while maintaining streamlined accessibility and minimizing user frustration.
How Do I Secure My Azure Tenant?
Access security is one of the most pressing concerns with the data that is stored in Power BI.
You can implement several safeguards to ensure that data is only accessible by members that are a part of your organization’s Azure Active Directory (AD) or Office 365 environment.
Secure Authentication
Power BI leverages Azure Active Directory (AD) or Office 365 (O365) for secure authentication and login, offering a comprehensive security system of user accounts, roles, access policies, and more.
This streamlined connection with Office 365 applications such as SharePoint Online and Exchange Online also provides instant setup for users when they login to Power BI.
Advanced Security Measures
Azure AD features several built-in Power BI security enhancements, including MFA and user access controls. You can also leverage role-based access controls (RBAC) to limit access to the data, and what actions can be performed.
Features like Azure Information Protection, Azure Conditional Access, and Azure Security Center provide further tools and measures to protect sensitive data, determine access, and detect vulnerabilities and threats.
With increasingly sophisticated conditional access settings, organizations can protect their Azure AD and O365 environments with layers of security such as IP address restriction, device-specific restrictions, and group-based access.
However, organizations should still regularly monitor for suspicious activity to ensure these conditions remain effective.
Additional Resources on Power BI Access Security:
Enterprise Deployment White Paper
What Are the Advantages of Workspaces in Power BI?
With separate Power BI workspaces, administrators can control the creation and publishing of datasets, reports, and dashboards to Active Directory Groups.
Azure AD Security groups should be created for users to define who can create workspaces. Additionally, teams need to configure Power BI tenant settings to be enabled ONLY for the workspace creators.
Power BI workspace roles should be utilized to control who has access to the workspace, and what privileges are granted.
The chart below helps visualize capabilities by role:
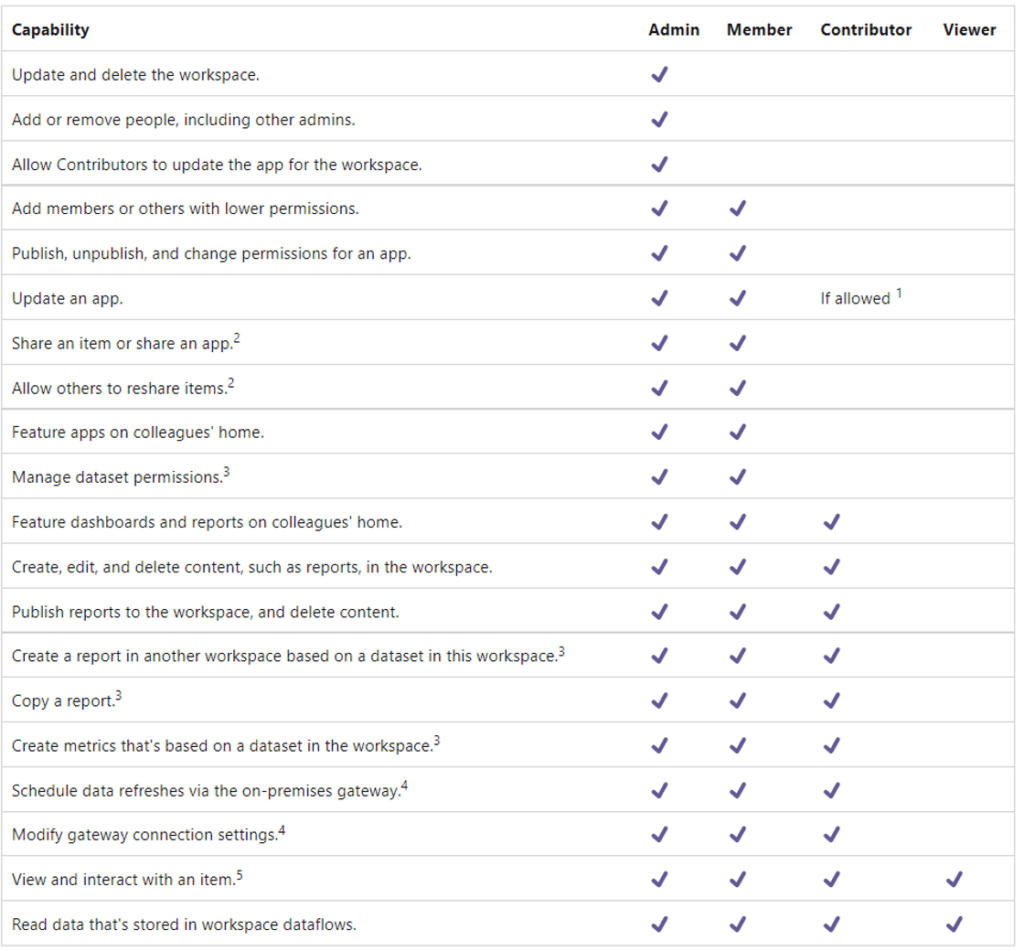
Use Azure AD or O365 Groups for the Following:
Defining User Permissions
You can use groups to define the level of access that users have to different Power BI resources.
For example, you can create a group for report creators and assign users to that group if you want them to be able to create and publish reports.
Managing Content Distribution
Groups can be used to distribute content to specific users or groups of users.
For example, you can create a group for a specific department, and then share dashboards and reports with that group, rather than sharing them with individual users.
Controlling Access to Data Sources
You can use groups to control access to data sources that are used in Power BI reports and dashboards.
For example, you can create a group for users who need access to a specific data source, and then grant access to that data source only to users in that group.
Managing Access to Features
You can use groups to manage access to features in Power BI, such as creating and publishing reports, or editing dashboards.
Managing Access to Workspaces
You can use groups to manage access to workspaces in Power BI, which are used to organize and share content.
For example, you can create a group for a specific project, and then assign users to that group to give them access to the project workspace.
Additional Resources on Workspaces:
Enterprise Deployment White Paper
Can Azure Active Directory Replace On-Premise for Power BI Permission Settings?
Onsite Active Directory and Azure AD can both be used to manage Power BI permissions, but the ideal option depends entirely on the requirements of your organization.
Onsite AD is the best method for managing users for organizations with on-prem resources that prefer to keep all the user management and authentication in-house.
Azure AD’s cloud-based identity and access management can be used for organizations with a combination of on-prem and cloud-based infrastructure. The ability to manage both on-prem and cloud-based permissions within a single identity management solution is a huge benefit of utilizing Azure AD.
Azure AD also provides seamless integration with other Azure services, including Office 365. Azure AD features like MFA and conditional access further strengthen the security of Power BI.
This comparison table summarizes the main differences between Onsite Active Directory and Azure Active Directory for managing permissions in Power BI:
| Feature | Onsite Active Directory | Azure Active Directory |
| Location | On-premises | Cloud-based |
| Integration with other on-premises applications | Easy | More complex |
| Integration with Azure services | More complex | Easy |
| Additional features | Fewer | More (e.g. multi-factor authentication, conditional access) |
| Scalability | Limited by on-premises infrastructure | Scalable with cloud infrastructure |
Additional Resources on Azure Active Directory:
What is Azure Active Directory and Why You Need It
What is the Best Way to Implement Writeback in Power BI?
Power BI does not provide any “out of the box” write-back capabilities to your data warehouse. However, Power Apps can be used in conjunction with Power BI to create write-back solutions.
You have multiple control points, but the ultimate preventative measure would be user restrictions at the data source (i.e. SQL Server).
Additional Resources on Writeback in Power BI:
Power BI data write-back with Power Apps and Power Automate
How to Implement Writeback Comments in Power BI Using Power Apps
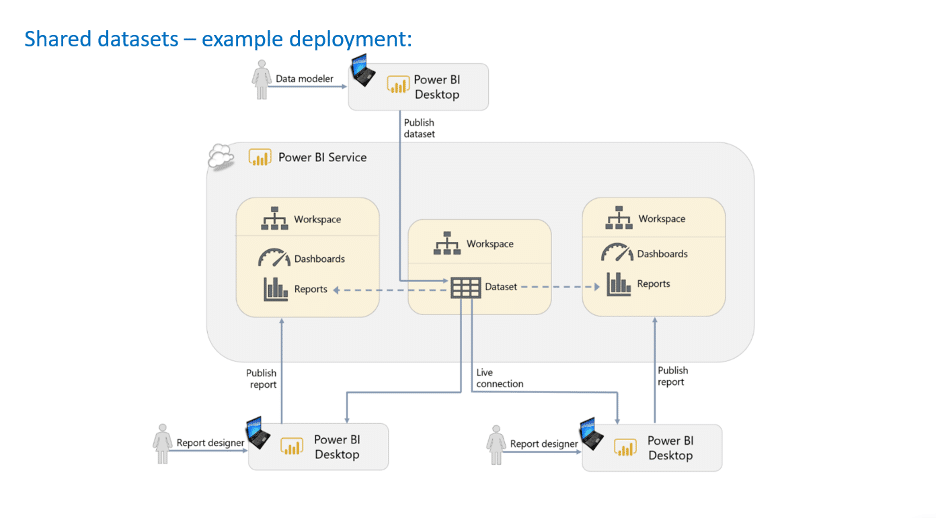
What Are the Benefits of Shared Datasets in Power BI?
Consider using Shared/Certified datasets wherever possible. In Power BI, a shared dataset is a single dataset used by multiple reports in various workspaces.
Shared datasets have several benefits, including:
Reusing Data
By using a shared dataset, you can easily reuse the same data in multiple reports and dashboards, which can save you time and effort, and reduces the proliferation of datasets.
Consistency
Using a shared dataset ensures that all reports and dashboards are using the same underlying data, which helps to ensure consistency and accuracy in your analyses.
Collaboration
Shared datasets can be used to facilitate collaboration among team members, as multiple users can access and use the same dataset.
Data Security
Shared datasets can be used to control access to data, as you can set permissions designating who can view and edit the dataset.
Limited Backend Access
Reusable datasets mean that fewer people will need access to the backend data systems.
Additional Resources on Shared Datasets:
Introduction to Datasets Across Workspaces
How Do I Manage Permissions in Power BI Workspaces?
There are several access standards to help you control which teams/individuals have access to certain workspaces.
Workspaces organization schemes will vary based on several factors, including:
- Subject matter content
- Teams
- Projects
- Specific Reports
- Departments
- Audiences
For your team, consider creating an AD Group, and set a standard policy that your Group is always added as a Workspace Member.
A Power BI Admin can add Members (Groups) to any workspace using the Workspace management feature in the Admin Portal.
Additional Resources on Power BI Workspaces:
Manage Workspaces from the Admin Portal
How Do I Manage App Permissions in Power BI?
As a more advanced permissions management capability, you can control who has access to the mobile app as well as the desktop platform.
In Power BI, access to the mobile app is controlled through Azure AD Roles and Row-Level Security (RLS).
Power BI Administrators can control access to mobile app access at the organizational level, where Member, Admin, and Contributor roles can be assigned. Specific groups of users can be granted access to Mobile App access, while other groups can be restricted.
Row-level security allows the restriction of data access at the row level based on the user’s role, allowing granular control over which users can see specific data in a report.
Additional Resources App Permissions:
The Perks of Maximizing Your Power BI Security
Understanding these frequent questions, pitfalls, and best practices, will empower your organization to remove friction for seamless user experiences, extend the power of data visualization to the right people, all while adhering to data security and data governance best practices.
If you or your organization is interested in furthering your business intelligence journey leveraging Power BI, be sure to check out Skypoint Cloud’s industry-leading thought leadership, pre-packaged product enhancements, and other free resources.
We put together a comprehensive list of our most high-value assets below to get you started: